Comparing Timelines
Exploring the overlapping histories of "Industrial Revolution" and "American Revolution".

Industrial Revolution
1700 - 1930

American Revolution
1763 - 1791
1698 CE
Thomas Savery patents steam pump
Thomas Savery patented the first commercially successful industrial use of steam power in 1698. His low-lift combined vacuum and pressure water pump generated about one horsepower and was used in waterworks and mines, marking the beginning of steam power applications.
1701 CE
Jethro Tull's mechanical seed drill developed
Jethro Tull's mechanical seed drill was developed in the early 18th century (around 1701), ensuring more even sowing and depth control. This agricultural innovation was part of the British Agricultural Revolution that supported industrial development by increasing food production efficiency.
1704 CE
John Harris publishes Lexicon Technicum
John Harris published the Lexicon Technicum, offering extensive scientific and engineering entries. This technical encyclopedia helped disseminate industrial methods and knowledge, contributing to the spread of technological innovation during the early Industrial Revolution.
1709 CE
Abraham Darby uses coke in blast furnaces
Abraham Darby made progress using coke to fuel his blast furnaces at Coalbrookdale. This innovation began the transition from charcoal to coke in iron production, though the coke pig iron was initially only suitable for cast iron goods rather than wrought iron.
1712 CE
Thomas Newcomen introduces steam engine
Thomas Newcomen introduced the first successful piston steam engine before 1712. These engines were installed for draining deep mines and represented the first practical application of steam power, though they were extremely inefficient by modern standards.

Newcomen's steam-powered atmospheric engine
Newcomen's steam-powered atmospheric engine was the first practical piston steam engine; subsequent steam engines were to power the Industrial Revolution.
1721 CE
John Lombe's silk mill becomes operational
John Lombe's water-powered silk mill at Derby became operational, arguably the first highly mechanised factory. Lombe had learned silk thread manufacturing by acting as an industrial spy in Italy, representing early technology transfer and industrial espionage.

John Lombe's silk mill site today in Derby
John Lombe's silk mill site today in Derby, rebuilt as Derby Silk Mill
1730 CE
Joseph Foljambe develops iron Rotherham plough
Joseph Foljambe developed the iron Rotherham plough around 1730. This agricultural innovation was part of the British Agricultural Revolution that increased crop yields and released labor for industrial employment, supporting the broader Industrial Revolution.
1733 CE
John Kay patents the flying shuttle
John Kay patented the flying shuttle in 1733, which doubled the output of a weaver. This innovation worsened the imbalance between spinning and weaving, creating pressure for further technological developments in textile production.
1740 CE
Benjamin Huntsman develops crucible steel technique
Benjamin Huntsman developed his crucible steel technique in the 1740s. This improvement in steel production was crucial as steel was an expensive commodity used only where iron would not suffice, such as for cutting edge tools and springs.
1743 CE
Factory opens in Northampton with Paul and Wyatt's machines
A factory opened in Northampton with 50 spindles on each of five of Paul and Wyatt's machines. Lewis Paul had patented the roller spinning frame and flyer-and-bobbin system, representing early mechanization of textile production.
1748 CE
Paul and Bourn patent carding machines
Paul and Bourn patented carding machines in 1748. Based on two sets of rollers that travelled at different speeds, this technology was later used in the first cotton spinning mill, advancing textile mechanization.
1757 CE
John Wilkinson patents hydraulic powered blowing engine
Ironmaster John Wilkinson patented a hydraulic powered blowing engine for blast furnaces in 1757. This innovation improved the efficiency of iron production by providing better blast power for furnaces.
1760 CE
Industrial Revolution begins in Great Britain
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain around 1760, marking the start of a transitional period toward more widespread, efficient manufacturing processes. This transformation included the shift from hand production to machines and the rise of the mechanized factory system.
Cast iron blowing cylinder first used
The cast iron blowing cylinder was first used in 1760, improving blast furnace operations. This innovation allowed for higher blast furnace temperatures and increased iron production efficiency.
Hamleys toy store opens in London
Hamleys, the oldest toy store, opened in London in 1760. This represents the growth of consumer retail businesses during the Industrial Revolution, as rising prosperity created new markets for consumer goods.
1761 CE
Bridgewater Canal opens
The Bridgewater Canal in North West England opened in 1761, proving hugely commercially successful. From Worsley to Manchester, it cost £168,000 but reduced coal prices in Manchester by half within one year, inspiring Canal Mania across Britain.

The Bridgewater Canal
The Bridgewater Canal, which proved very commercially successful, crossed the Manchester Ship Canal, one of the last canals to be built.
1763 CE
End of French and Indian War
The French and Indian War concluded, leaving Britain with massive debt and new territorial responsibilities. This war's aftermath led to increased British taxation and control over the American colonies, setting the stage for colonial discontent and eventual revolution.
Royal Proclamation of 1763
The British government issued the Royal Proclamation designating territory between the Appalachian Mountains and Mississippi River as an Indian Reserve closed to settlement. This angered colonists who wanted to expand westward and failed to stop their migration.

File:Map_of_territorial_growth_1775.svg
A 1775 map of Eastern North America, including the Province of Quebec, the Thirteen Colonies on the Atlantic Coast, and the Indian Reserve as defined by the Royal Proclamation of 1763.
1764 CE
James Hargreaves invents the spinning jenny
James Hargreaves invented the spinning jenny in Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire in 1764. It was the first practical spinning frame with multiple spindles, revolutionizing textile production by allowing one worker to spin multiple threads simultaneously.

A model of the spinning jenny in a museum in Wuppertal
Invented by James Hargreaves in 1764, the spinning jenny was one of the innovations that started the revolution.
Sugar Act Passed
Parliament passed the Sugar Act, decreasing existing customs duties on sugar and molasses but providing stricter enforcement measures. This was part of Britain's effort to raise revenue from the colonies to help pay for the costs of maintaining troops in North America.
1765 CE
Stamp Act Passed
Parliament passed the Stamp Act, imposing direct taxes on the colonies for the first time. All official documents, newspapers, and pamphlets required stamps. Colonists objected not to the tax amount but to taxation without representation in Parliament, leading to the formation of the Sons of Liberty.

File:Parliament_Stamp_Act1765.jpg
Notice of the Stamp Act 1765 in a colonial newspaper
Stamp Act Congress
Representatives from nine colonies convened in New York City for the Stamp Act Congress. They issued a Declaration of Rights and Grievances arguing that taxation without representation violated their rights as Englishmen, establishing the principle of colonial unity against British policies.
1766 CE
Stamp Act Repealed
Parliament repealed the Stamp Act after colonial resistance and Benjamin Franklin's testimony about colonial contributions to the empire. However, they simultaneously passed the Declaratory Act asserting their right to make laws for the colonies 'in all cases whatsoever.'
1767 CE
Townshend Acts Passed
Parliament passed the Townshend Acts, placing duties on paper, glass, and tea, and establishing a Board of Customs in Boston. The goal was to assert British authority over the colonies rather than simply collect revenue, leading to renewed colonial resistance and boycotts.

File:Dickinson's_Letter_III_in_The_Pennsylvania_Chronicle.jpg
Letter III of John Dickinson's Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania, published in the Pennsylvania Chronicle, December 1767
1768 CE
Cast iron blowing cylinder used at Carrington
The first blowing cylinder made of cast iron is believed to be the one used at Carrington in 1768, designed by John Smeaton. This advancement improved blast furnace efficiency and iron production capacity.
1769 CE
Richard Arkwright patents the water frame
Richard Arkwright patented the water frame in 1769, which could produce hard, medium-count thread suitable for warp. This finally allowed 100% cotton cloth to be made in Britain, revolutionizing textile production.
1770 CE
Boston Massacre
British soldiers fired into a threatening crowd on a Boston street, killing five civilians including Crispus Attucks. Though the soldiers were acquitted, the event was used as propaganda against British rule and accelerated the deterioration of British-colonial relations.
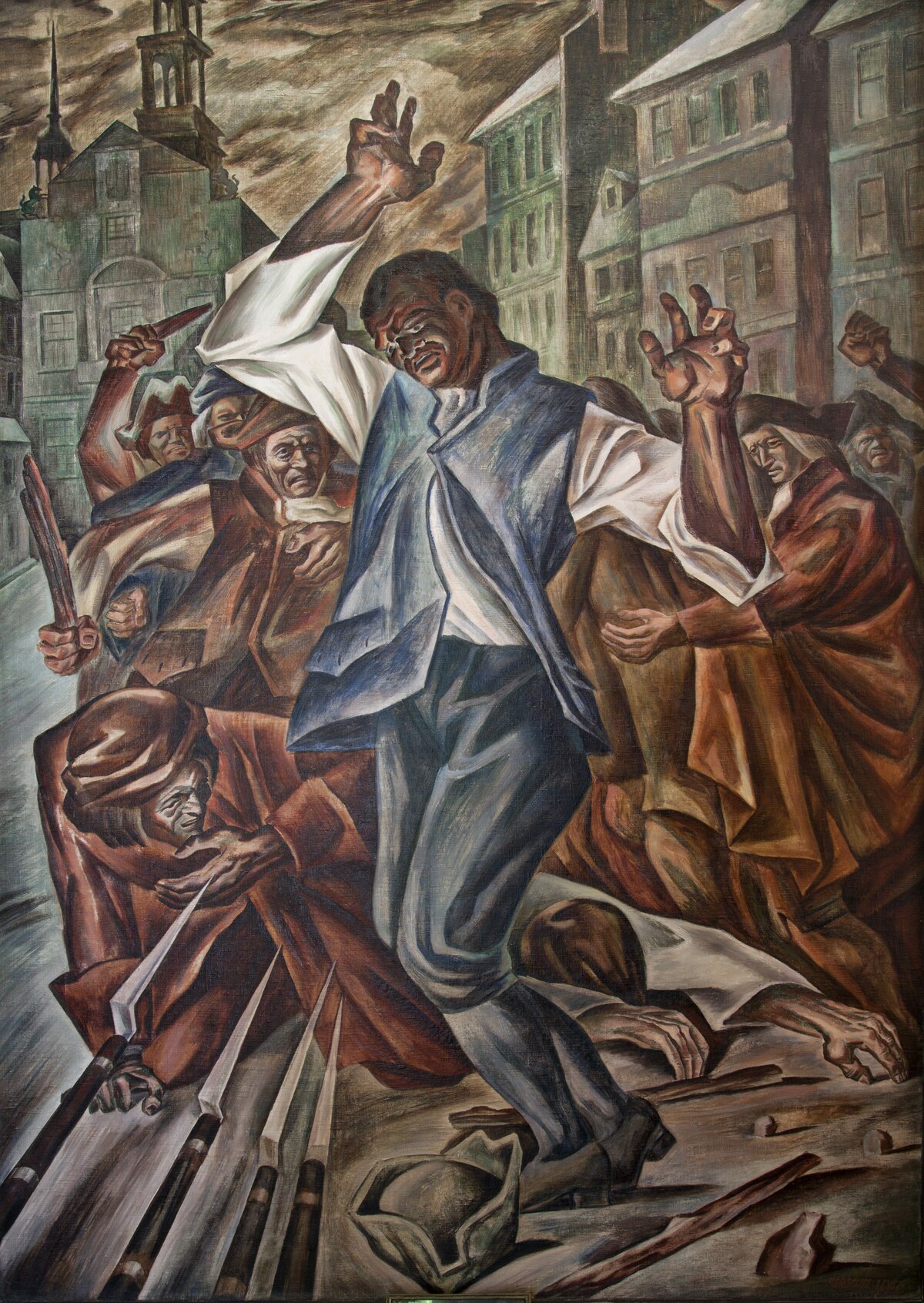

"Crispus_Attucks,"_by_Herschel_Levit
Crispus Attucks, a portrait by Herschel Levit depicts Attucks, who is considered to be the first American to die for the cause of independence in the Revolution.
1771 CE
Arkwright establishes water-powered factory at Cromford
Richard Arkwright used water power at a factory in Cromford, Derbyshire in 1771, giving the water frame its name. This represented the establishment of the factory system and mechanized production methods.
1772 CE
Gaspee Affair
American patriots including John Brown burned HMS Gaspee, a British customs schooner that had been vigorously enforcing unpopular trade regulations in Narragansett Bay. The affair was investigated for possible treason but no action was taken, showing colonial willingness to use violence against British authority.

File:Destruction_of_the_schooner_Gaspé
On June 9, 1772, the Sons of Liberty burned HMS Gaspee, a British customs schooner in Narragansett Bay.
1773 CE
Tea Act Passed
Parliament passed the Tea Act to help the struggling British East India Company by allowing it to sell tea directly to colonists at reduced prices, bypassing colonial merchants. This threatened colonial merchants and was seen as another attempt to assert British control over colonial trade.
Boston Tea Party
Led by Samuel Adams, a group of men disguised as Indigenous people boarded East India Company ships and dumped £10,000 worth of tea into Boston Harbor. This act of defiance against the Tea Act became a symbol of American resistance to British taxation and authority.

File:Boston_Tea_Party_w.jpg
The December 16, 1773 Boston Tea Party, led by Samuel Adams and Sons of Liberty, has become a mainstay of American patriotic lore.
1774 CE
John Wilkinson invents cylinder boring machine
John Wilkinson invented a machine for boring cylinders in 1774. This was the first large precision machine tool and was crucial for manufacturing steam engine cylinders, enabling the development of more efficient steam engines.
Leeds and Liverpool Canal opens
The Leeds and Liverpool Canal opened in 1774, becoming one of the most notable canals built during Canal Mania. This canal connected major industrial centers and facilitated the transport of raw materials and finished goods.
Intolerable Acts Passed
Parliament responded to the Boston Tea Party by passing four punitive laws: the Massachusetts Government Act, Administration of Justice Act, Boston Port Act, and Quartering Act. These acts further darkened colonial opinion toward Britain and united the colonies in opposition.
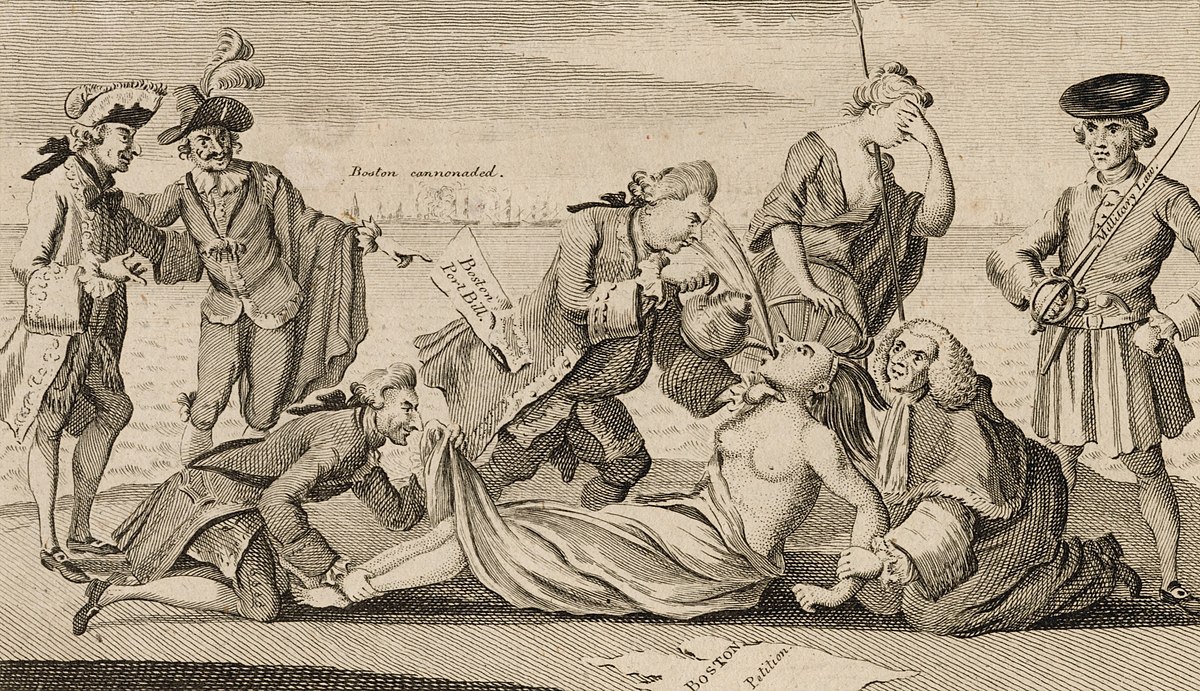

File:The_able_doctor
A 1774 illustration from The London Magazine depicts Prime Minister Lord North, author of the Boston Port Act, forcing the Intolerable Acts down the throat of America.
First Continental Congress
Representatives from twelve colonies convened in Philadelphia to coordinate resistance to British policies. They called for a boycott of British goods and began organizing Patriot resistance through local committees, marking the first unified colonial response to British authority.
1775 CE
King George III Declares Massachusetts in Rebellion
King George III officially declared Massachusetts to be in a state of rebellion, escalating the conflict between Britain and the colonies. This declaration marked the transition from political protest to open confrontation and set the stage for military action.
Battles of Lexington and Concord
British attempts to seize colonial weapons and arrest Patriot leaders resulted in the first military engagements of the Revolutionary War. The 'shot heard 'round the world' marked the beginning of armed conflict between Britain and the American colonies.

File:Prince_Estabrook_memorial_close_up.jpg
A Lexington, Massachusetts memorial to Prince Estabrook, who was wounded in the Battle of Lexington and Concord and was the first Black casualty of the Revolutionary War
Second Continental Congress Convenes
The Second Continental Congress convened in Philadelphia to manage the colonial war effort. They authorized the formation of the Continental Army and appointed George Washington as commander-in-chief, while also attempting reconciliation through the Olive Branch Petition.
Battle of Bunker Hill
British forces achieved a costly victory against entrenched American forces, suffering about 1,000 casualties from a garrison of 6,000 compared to 500 American casualties. The heavy British losses demonstrated that colonial forces could inflict serious damage on professional troops.

File:00SalemPoor.jpg
A postage stamp, created at the time of the bicentennial, honors Salem Poor, who was an enslaved African American man who purchased his freedom, became a soldier, and rose to fame as a war hero during the Battle of Bunker Hill.
Dunmore's Proclamation
Virginia's royal governor Lord Dunmore issued a proclamation offering freedom to slaves who would join British forces. This recruitment of Black soldiers angered Southern Patriots and played a major role in Southern support for independence, as colonists feared slave rebellions.
1776 CE
Wilkinson bores first successful cylinder for Watt engine
John Wilkinson bored the first successful cylinder for a Boulton and Watt steam engine in 1776, leading to an exclusive contract for providing cylinders. This precision manufacturing was crucial for steam engine development.
New Hampshire Ratifies First State Constitution
New Hampshire became the first colony to ratify a state constitution, beginning the process of creating new republican governments to replace royal authority. This marked the transition from colonial governments to independent state governments.
British Evacuate Boston
George Washington's Continental Army, aided by cannons from Fort Ticonderoga, forced British forces to evacuate Boston by sea. This victory gave Patriots control of all thirteen colonies and demonstrated the effectiveness of the Continental Army under Washington's leadership.
Congress Votes to Suppress Crown Authority
The Continental Congress voted to suppress all forms of Crown authority in the colonies, to be replaced by locally created authority. This decisive step toward independence encouraged colonies to create their own state constitutions and governments.
Lee Resolution Passed
The Continental Congress passed the Lee Resolution affirming their support for joint independence from Britain. This resolution set the stage for the formal Declaration of Independence and represented the colonies' commitment to complete separation from British rule.
Declaration of Independence Adopted
The Continental Congress unanimously adopted the Declaration of Independence, drafted largely by Thomas Jefferson. The document proclaimed that 'all men are created equal' and established the philosophical foundation for American independence based on natural rights and consent of the governed.

File:William_Walcutt_statue_George_III.png
Pulling Down the Statue of King George III, N.Y.C., depicting American patriots tearing down a statue of King George III in New York City on July 9, 1776, five days after the adoption of the Declaration of Independence.
Battle of Brooklyn
British forces defeated Washington's Continental Army in the largest battle of the Revolutionary War. The British victory nearly captured Washington's army and demonstrated British military superiority, but Washington's successful retreat prevented total disaster.

File:The British fleet in the lower bay 1876.jpg
The British fleet amassed off Staten Island in New York Harbor in the summer of 1776, as depicted in Harper's Magazine in 1876
Staten Island Peace Conference
A delegation including John Adams and Benjamin Franklin met with British Admiral Richard Howe to negotiate an end to hostilities. The British demanded retraction of the Declaration of Independence, which the Americans refused, ending hopes for peaceful resolution.
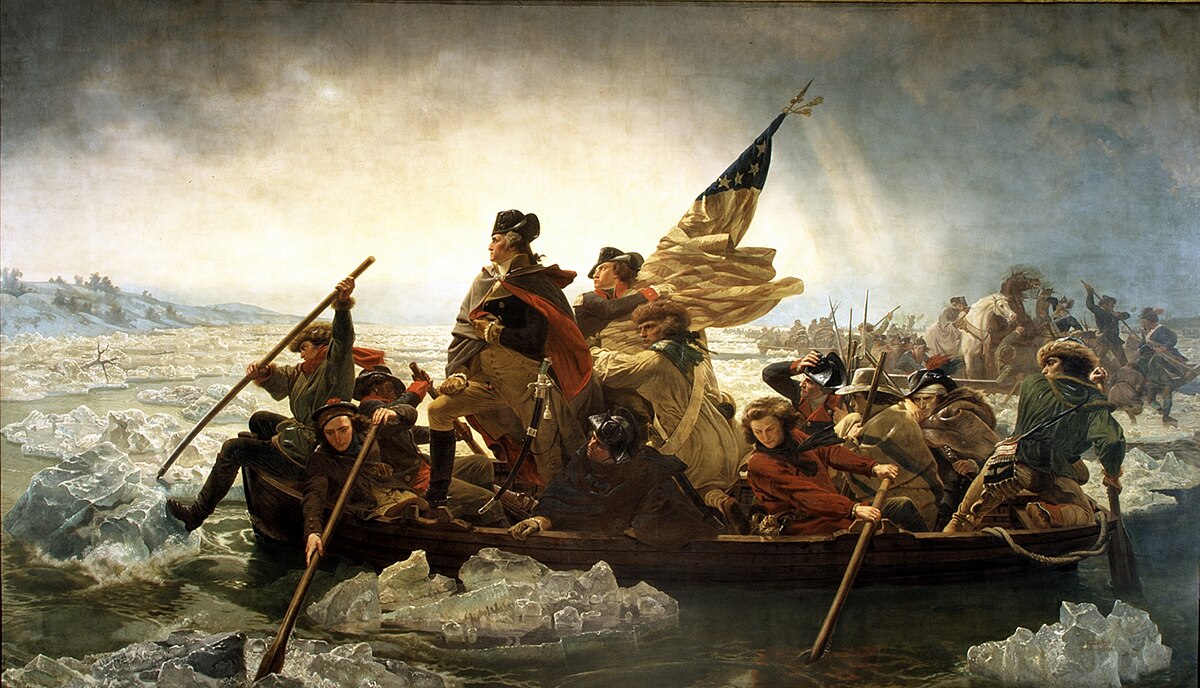
Washington Crosses the Delaware
Washington led a surprise attack across the Delaware River, defeating Hessian and British troops at Trenton and Princeton. These victories regained control of most of New Jersey and provided a crucial morale boost to the Patriot cause during a dark period of the war.

File:Washington Crossing the Delaware by Emanuel Leutze, MMA-NYC, 1851.jpg
Washington crossing the Delaware on December 25–26, 1776, depicted in Emanuel Leutze's 1851 painting
1777 CE
Battles of Saratoga
American forces defeated British General Burgoyne's invasion army, forcing its surrender. This decisive victory convinced France to formally enter the war as an American ally, transforming the conflict into a global war and providing crucial support for American independence.
Articles of Confederation Approved
Congress approved the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, creating the first constitution for the United States. The Articles established a confederation of sovereign states with a weak central government, providing structure during the Revolutionary War.
1778 CE
Iron Bridge opens in Shropshire
The Iron Bridge opened in 1778, built with cast iron produced by Abraham Darby III. This was the world's first bridge constructed of iron and demonstrated the structural potential of cast iron as a building material.

The Iron Bridge in Shropshire, England
The Iron Bridge in Shropshire, England, the world's first bridge constructed of iron, opened in 1781.
James Watt perfects his steam engine
James Watt, with financial support from Matthew Boulton, perfected his steam engine by 1778. The engine incorporated radical improvements including a separate steam condenser chamber, increasing efficiency dramatically and using only 20-25% as much coal as Newcomen's engines.

A Watt steam engine
A Watt steam engine, invented by James Watt, who transformed the steam engine from a reciprocating motion that was used for pumping to a rotating motion suited to industrial applications
Treaty of Alliance with France
The United States and France signed the Treaty of Amity and Commerce and the Treaty of Alliance, making France the first foreign nation to officially recognize American independence. This alliance provided crucial military and financial support for the American war effort.

File:LouisXVI-France1.jpg
Louis XVI, King of France and Navarre
1779 CE
Samuel Crompton invents the spinning mule
Samuel Crompton invented the spinning mule in 1779, a hybrid of Arkwright's water frame and Hargreaves's spinning jenny. The mule could produce finer thread than hand spinning at lower cost and was suitable for use as warp, allowing Britain to produce highly competitive yarn.

The only surviving example of a spinning mule built by Samuel Crompton
The only surviving example of a spinning mule built by the inventor Samuel Crompton, the mule produced high-quality thread with minimal labour, now on display at Bolton Museum in Greater Manchester
Philipsburg Proclamation
British forces expanded their promise of freedom to all enslaved people in rebellious colonies who enlisted in British military service. This proclamation significantly increased the number of Black Loyalists and further angered Southern Patriots who feared losing their enslaved workforce.
Spain Declares War on Britain
Spain formally declared war on Britain as a French ally, opening new fronts in the global conflict. Spanish forces under Bernardo de Gálvez captured Florida from the British and kept vital supply lines open to the Americans.
1780 CE
British Capture Charleston
British forces captured Charleston, South Carolina, in their largest victory of the southern campaign. This success gave Britain control of most of Georgia and South Carolina and marked the height of British military success in the South.
1781 CE
Iron Bridge officially opens
The Iron Bridge in Shropshire officially opened in 1781, becoming the world's first bridge constructed entirely of iron. This landmark engineering achievement demonstrated the structural capabilities of cast iron and influenced future construction methods.
Articles of Confederation Ratified
The Articles of Confederation were fully ratified by all thirteen states, officially establishing the United States government. The Continental Congress was dissolved and replaced by the United States in Congress Assembled under the new constitution.
Siege of Yorktown
Combined French and American forces under Washington besieged British General Cornwallis at Yorktown. The French naval victory in the Battle of the Chesapeake trapped Cornwallis, leading to his surrender and effectively ending major combat operations in the Revolutionary War.
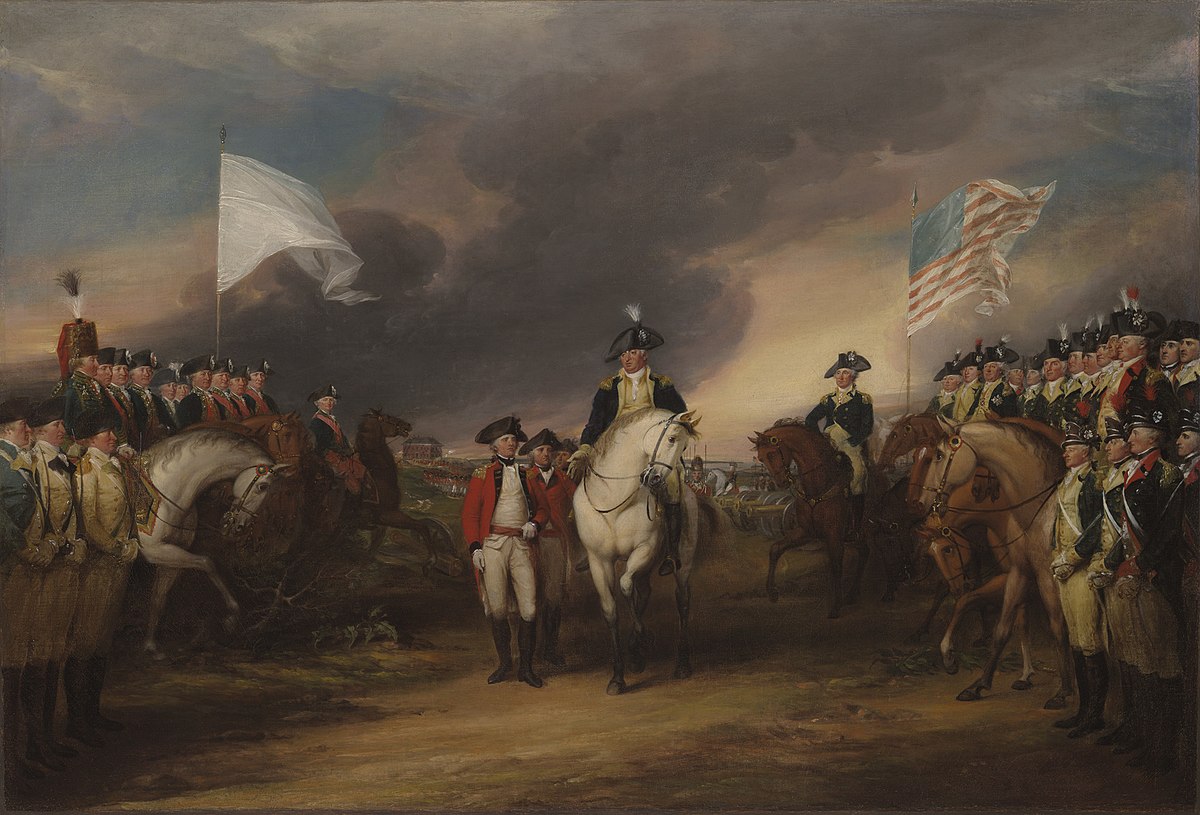

File:John_Trumbull_-_The_Surrender_of_Lord_Cornwallis_at_Yorktown
The 1781 siege of Yorktown ended with the surrender of a second British army, marking effective British defeat.
1782 CE
Watt develops rotary steam engine
James Watt developed a rotary steam engine in 1782, which could directly drive factory machinery. This innovation made steam power widely applicable to industrial processes including blowing, hammering, rolling and slitting operations.
1783 CE
Henry Cort develops rolling process
Henry Cort developed the rolling process in 1783, which was fifteen times faster than hammering wrought iron. This innovation significantly improved the efficiency of iron production and processing.
Watt steam engine becomes double-acting rotative type
The Watt steam engine was fully developed into a double-acting rotative type in 1783, meaning it could directly drive rotary machinery in factories and mills. This advancement made steam power practical for widespread industrial use.
Treaty of Paris Signed
Britain signed the Treaty of Paris, formally ending the Revolutionary War and recognizing American independence. The treaty granted the United States all territory east of the Mississippi River and south of the Great Lakes, establishing the new nation's borders.

File:Treaty of Paris by Benjamin West 1783.jpg
Treaty of Paris by Benjamin West portrays the American delegation about to sign the 1783 Treaty of Paris (John Jay, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Henry Laurens, W.T. Franklin). The British delegation refused to pose and the painting was never completed.
1784 CE
Henry Cort develops puddling process
Henry Cort developed the puddling process in 1784, which produced structural grade iron at relatively low cost. This process became widely used after 1800 and was crucial for producing high-quality wrought iron, though it was backbreaking work.
Andrew Meikle invents threshing machine
Andrew Meikle invented the threshing machine in 1784, which reduced manual labor requirements in agriculture. Hand threshing had taken about one-quarter of agricultural labor, so this innovation freed up workers for industrial employment.
1785 CE
Edmund Cartwright patents power loom
Edmund Cartwright developed and patented a vertical power loom in 1785. Realizing that the expiration of Arkwright's patent would increase cotton supply and create a weaver shortage, Cartwright's invention mechanized weaving to match spinning capacity.
Oliver Evans invents automated flour mill
Oliver Evans invented an automated flour mill in the mid-1780s that used control mechanisms and conveyors requiring no labor from grain loading to flour discharge. This is considered the first modern materials handling system and an important advance toward mass production.
1787 CE
Beverly Cotton Manufactory founded
Thomas Somers and the Cabot Brothers founded the Beverly Cotton Manufactory in 1787, the first cotton mill in America and the largest of its era. Though initially designed for horsepower, it served as a playground of innovation for cotton processing.
Constitutional Convention
Delegates from twelve states convened in Philadelphia to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. Instead of revising the Articles, they drafted an entirely new Constitution creating a stronger federal government with executive, legislative, and judicial branches.

File:Scene_at_the_Signing_of_the_Constitution_of_the_United_States.jpg
The September 17, 1787 signing of the United States Constitution at Independence Hall in Philadelphia depicted in Howard Chandler Christy's 1940 painting, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States
1788 CE
Constitution Ratified
The new Constitution was ratified by the required nine states, replacing the Articles of Confederation. The Constitution established a federal republic with a strong national government while preserving state rights, creating the framework for modern American government.
1789 CE
Thames and Severn Canal opens
The Thames and Severn Canal opened in 1789, connecting major waterways and facilitating trade and transport. This canal was part of the broader canal building boom that transformed Britain's transportation infrastructure during the Industrial Revolution.
George Washington Inaugurated
George Washington was inaugurated as the first President of the United States under the new Constitution. His presidency established important precedents for the executive branch and demonstrated the peaceful transfer of power in the new republic.
1791 CE
Nicolas Leblanc introduces soda ash production method
Nicolas Leblanc succeeded in introducing a method for large-scale production of sodium carbonate (soda ash) in 1791. The Leblanc process enabled mass production of this important chemical used in glass, textile, soap, and paper industries.
Prague hosts first World's Fair
Prague hosted the first World's Fair in 1791 in Clementinum, showcasing the region's growing industrial sophistication. This exhibition celebrated advanced manufacturing techniques in the Czech lands and demonstrated the spread of industrialization beyond Britain.
Bill of Rights Ratified
The first ten amendments to the Constitution, known as the Bill of Rights, were ratified. These amendments guaranteed fundamental individual rights and freedoms, addressing concerns about federal power and fulfilling promises made during the ratification debates.
1792 CE
Eli Whitney invents cotton gin
Eli Whitney invented the cotton gin in 1792, which could remove seed from cotton 50 times faster than by hand. This invention made upland cotton profitable and led to the massive expansion of slave plantations in the American South.
1793 CE
Samuel Slater founds Slater Mill
Samuel Slater founded Slater Mill at Pawtucket, Rhode Island in 1793. Having learned textile technologies as an apprentice in England, Slater defied laws against skilled worker emigration and established one of America's first successful textile mills.
Slater's Mill in Pawtucket, Rhode Island
Slater's Mill in Pawtucket, Rhode Island
1795 CE
Boulton and Watt open Soho Foundry
Boulton and Watt opened the Soho Foundry for the manufacture of steam engines in 1795. This facility became a major center for steam engine production and helped spread steam technology throughout Britain and beyond.
1796 CE
Harding, Howell & Co. opens first department store
Harding, Howell & Co. opened one of the first department stores in 1796 on Pall Mall, London. This represented the evolution of retail during the Industrial Revolution as rising prosperity created demand for diverse consumer goods in centralized locations.
1798 CE
Louis-Nicolas Robert patents paper machine
Louis-Nicolas Robert patented a machine for making continuous sheet paper on a loop of wire fabric in France in 1798. This innovation, later known as the Fourdrinier machine, revolutionized paper production and influenced other continuous production processes.
1799 CE
First use of 'Industrial Revolution' term
The earliest recorded use of 'Industrial Revolution' was in 1799 by French envoy Louis-Guillaume Otto, announcing that France had entered the race to industrialize. This marked the recognition of the transformative economic changes occurring across Europe.
1800 CE
Charles Tennant develops bleaching powder
Chemist Charles Tennant developed bleaching powder (calcium hypochlorite) in 1800, based on Claude Louis Berthollet's discoveries. This revolutionized textile bleaching by reducing the time required from repeated sun exposure to a chemical process.
Boulton and Watt patent expires
The Boulton and Watt patent expired around 1800, allowing other inventors like Richard Trevithick and Oliver Evans to develop higher-pressure steam engines. This led to more compact engines suitable for mobile applications like locomotives and steamboats.
1801 CE
First mechanical loom introduced in Czech lands
The first mechanical loom in the Czech lands was introduced in Varnsdorf in 1801, followed shortly by steam engines in Bohemia and Moravia. This marked the beginning of industrialization in the Habsburg realms, with the Czech lands becoming the industrial hub.
1802 CE
Abraham Rees publishes The Cyclopaedia
Abraham Rees published The Cyclopaedia; or, Universal Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, and Literature between 1802-19. This technical encyclopedia contained detailed articles and engraved plates on machines and processes, helping disseminate industrial knowledge.
1806 CE
Cotton strain brought from Mexico to Natchez
A strain of cotton seed was brought from Mexico to Natchez, Mississippi in 1806, becoming the parent genetic material for 90% of world cotton production. This variety produced bolls three to four times faster to pick, revolutionizing cotton agriculture.
1809 CE
Daniel Day establishes wool carding mill
Daniel Day established a wool carding mill in the Blackstone Valley at Uxbridge, Massachusetts in 1809, the third woollen mill established in the US. This contributed to the development of America's textile industry in the Blackstone Valley region.
1811 CE
Luddite movement begins
The Luddite movement began in 1811 with attacks on textile machinery near Nottingham. Unemployed workers, unable to compete with machines, began destroying factories and equipment. The movement spread rapidly before being suppressed by military force.
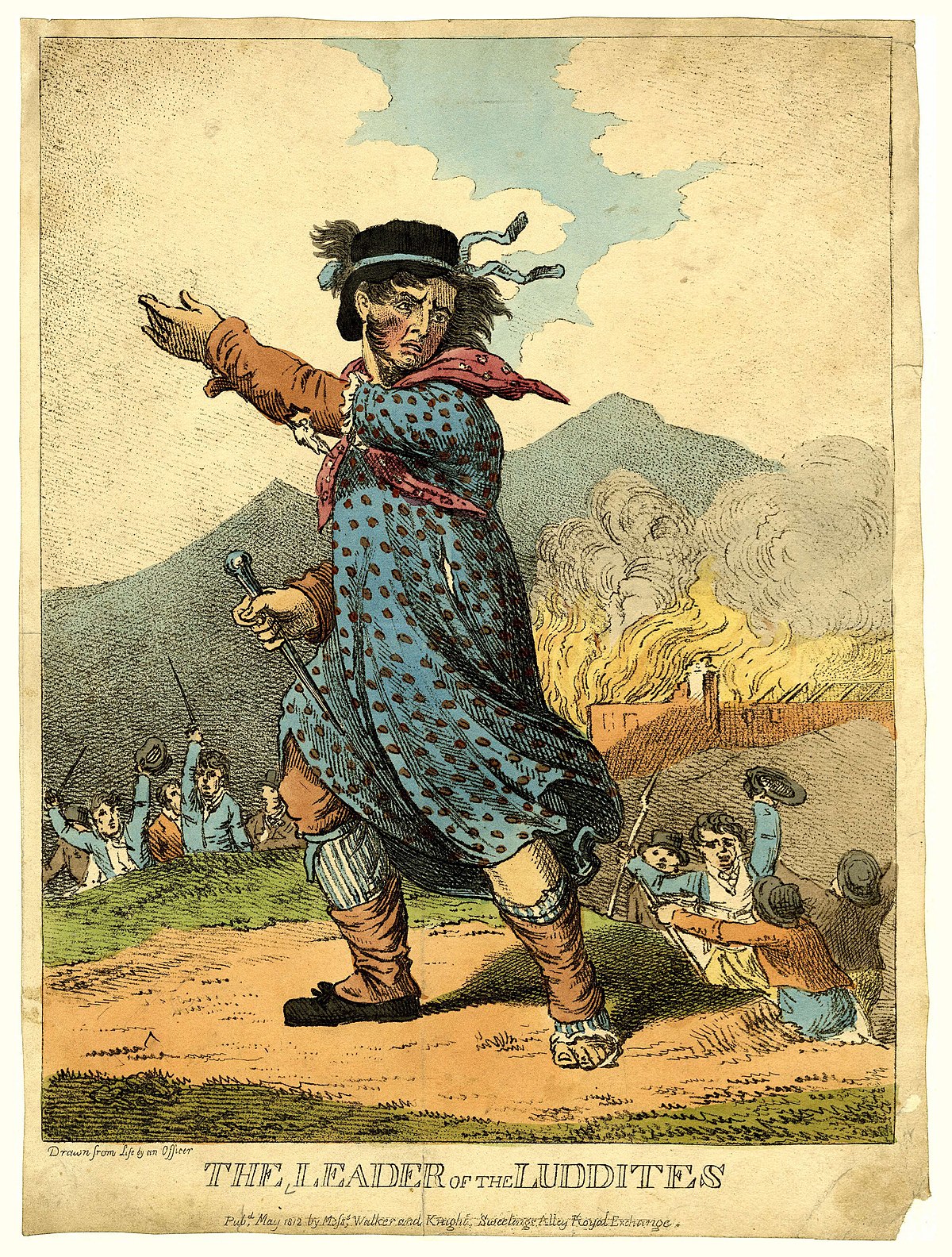

Engraving of Ned Ludd, Leader of the Luddites, 1812
Engraving of Ned Ludd, Leader of the Luddites, 1812
1812 CE
Gas lighting utilities established in London
The first gas lighting utilities were established in London between 1812 and 1820. Gas lighting allowed factories and stores to remain open longer and enabled nightlife to flourish in cities, fundamentally changing social and industrial organization.
1813 CE
Samuel Horrocks patents improved loom
Samuel Horrocks patented an improved loom in 1813, which was later enhanced by Richard Roberts in 1822. These looms were produced in large numbers by Roberts, Hill & Co., advancing textile manufacturing efficiency.
1815 CE
Corn Laws enacted in Britain
The Corn Laws were enacted in Britain from 1815-46, imposing tariffs on imported grain to keep prices high for domestic producers. These laws adversely affected food supply and were eventually repealed during the Great Irish Famine.
1816 CE
Safety lamp invented
The safety lamp was invented in 1816 by Sir Humphry Davy, and independently by George Stephenson. This provided some protection against firedamp explosions in coal mines, though the lamps proved problematic and mining remained dangerous.
First macadam road built in Bristol
The first 'macadam' stretch of road was built as Marsh Road at Ashton Gate, Bristol in 1816. This new road construction method, developed by John McAdam, provided better, more durable roads for transportation.
1817 CE
Francis Cabot Lowell dies
Merchant Francis Cabot Lowell died in 1817 after establishing the Boston Manufacturing Company and America's second cotton-to-cloth textile mill at Waltham, Massachusetts. His associates later built America's first planned factory town named after him.
1818 CE
Middletown milling machine developed
The Middletown milling machine was developed around 1818 by Robert Johnson and Simeon North. This advancement in machine tools improved precision manufacturing capabilities and contributed to the development of interchangeable parts production.

The Middletown milling machine
The Middletown milling machine, developed around 1818 by Robert Johnson and Simeon North
1822 CE
Richard Roberts improves loom design
Richard Roberts improved Samuel Horrocks' loom design in 1822. Roberts was a maker of high-quality machine tools and pioneer in the use of jigs and gauges for precision workshop measurement, advancing manufacturing precision.
1823 CE
First macadam road in US completed
The first macadam road in the U.S., the 'Boonsborough Turnpike Road' between Hagerstown and Boonsboro, Maryland, was completed in 1823. This represented the adoption of British road-building technology in America.

Construction of the first macadam road in the U.S. in 1823
Construction of the first macadam road in the U.S. in 1823. In the foreground, workers are breaking stones "so as not to exceed 6 ounces in weight or to pass a two-inch ring".
1824 CE
Joseph Aspdin patents portland cement
Joseph Aspdin, a British bricklayer turned builder, patented a chemical process for making portland cement in 1824. This important advance in building trades involved sintering clay and limestone, then grinding it into powder for concrete production.
Combination Act repealed
The Combination Act of 1799, which forbade workers from forming trade unions, was repealed in 1824. This allowed workers to organize, though unions remained severely restricted and were viewed with suspicion by authorities and employers.
1825 CE
Stockton and Darlington Railway opens
Steam-hauled public railways began with the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. This marked the beginning of the railway age and demonstrated the practical application of steam locomotives for public transportation.
1828 CE
Hot blast development
Hot blast was developed in 1828, dramatically reducing fuel consumption in iron production. The 1828 development of hot blast, combined with other innovations, enabled the rapid expansion of railways by improving iron production capacity and efficiency.
James Beaumont Neilson patents hot blast
Scottish inventor James Beaumont Neilson patented hot blast in 1828, the most important 19th-century development for saving energy in pig iron production. It reduced fuel requirements by one-third using coke or two-thirds using coal.
1829 CE
Rainhill Trials demonstrate locomotive success
The Rainhill Trials in 1829 demonstrated Robert Stephenson's successful locomotive design. These trials proved the viability of steam locomotives and led to the rapid introduction of railways across Britain and beyond.
1830 CE
Belgium becomes independent
Belgium became independent in 1830, and especially after independence, factories comprising coke blast furnaces as well as puddling and rolling mills were built in coal mining areas around Liège and Charleroi, making Belgium the second country to industrialize.
Captain Swing disturbances affect southern Britain
The Captain Swing disturbances affected large parts of southern Britain in the 1830s as agricultural laborers protested industrialization. Threshing machines were particular targets, and hayrick burning was common, leading to the formation of trade unions.
Penny dreadfuls created
Penny dreadfuls were created in the 1830s to meet demand for cheap literature for the masses. These publications were 'Britain's first taste of mass-produced popular culture for the young' and 'the Victorian equivalent of video games.'
Major railway construction begins
Construction of major railways connecting larger cities and towns began in the 1830s, though it only gained momentum at the very end of the first Industrial Revolution. This marked the beginning of the railway boom that would transform transportation.
Liverpool and Manchester Railway opens
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway opened on September 15, 1830, becoming the first inter-city railway in the world. Engineered by Joseph Locke and George Stephenson, it linked Manchester with Liverpool and became highly successful, sparking Railway Mania.
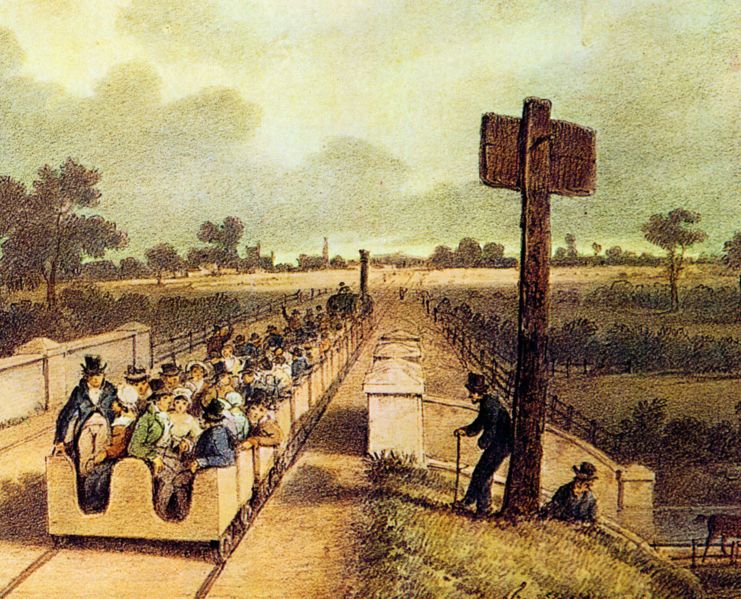
A portrait depicting the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway in 1830
A portrait depicting the opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway in 1830, the first inter-city railway in the world and which spawned Railway Mania due to its success
1832 CE
Chance Brothers use cylinder process for sheet glass
In 1832, the Chance Brothers used the cylinder process to create sheet glass, becoming leading producers of window and plate glass. This advancement allowed larger panes without interruption, revolutionizing architecture and interior design.
Reform Act extends voting rights
The Reform Act of 1832 extended voting rights in Britain, though it did not grant universal suffrage. This political reform was part of broader social changes accompanying industrialization, though working-class representation remained limited.
1833 CE
First Factory Acts passed
The first general laws against child labor, the Factory Acts, were passed in Britain in 1833. Children younger than nine were prohibited from working, night work was banned for children, and working hours for those under 18 were limited to 12 hours.
1834 CE
Tolpuddle Martyrs transported to Australia
Six men from Tolpuddle in Dorset, who founded the Friendly Society of Agricultural Labourers, were arrested, found guilty, and transported to Australia in 1834. They became known as the Tolpuddle Martyrs and symbolized early labor organization struggles.
1836 CE
Charles Dickens publishes The Pickwick Papers
Charles Dickens published The Pickwick Papers in 1836, which became a phenomenon and sparked spin-offs and merchandise. Dickens used innovations of the era including new printing presses, enhanced advertising, and railways to sell books, defining modern entertainment.
1837 CE
Jérôme-Adolphe Blanqui describes Industrial Revolution
Jérôme-Adolphe Blanqui provided a description of the Industrial Revolution in 1837, helping to popularize the term. His work contributed to the growing recognition and understanding of the economic transformation occurring across Europe.
1840 CE
Industrial Revolution spreads to continental Europe and US
By about 1840, the Industrial Revolution had spread from Great Britain to continental Europe and the United States. This marked the global expansion of industrialization beyond its British origins, transforming economies worldwide.
Uniform Penny Post introduced
The Uniform Penny Post was introduced in 1840 with the invention of the postage stamp (Penny Black), charging one penny for carriage between any two places in the UK. This revolutionized communication and enabled mail order business development.
Electrical telegraph widely introduced
The electrical telegraph was widely introduced in the 1840s in the UK and US. While this new technology improved communication, it was not sufficient alone to drive high rates of economic growth during this period.
1842 CE
General strike organized through Chartist movement
In 1842, a general strike involving cotton workers and colliers was organized through the Chartist movement, stopping production across Britain. This demonstrated the growing power of organized labor and working-class political movements.
Laws improve mine working conditions
Laws passed in 1842 and 1844 improved mine working conditions in Britain. The employment of children and women in mining was forbidden, and other safety measures were implemented to address the dangerous conditions in coal mines.
1843 CE
Thames Tunnel opens
The Thames Tunnel opened in 1843, becoming the world's first underwater tunnel. English engineer Marc Isambard Brunel used portland cement concrete in its construction, demonstrating new engineering capabilities and construction materials.

The Thames Tunnel, which opened in 1843
The Thames Tunnel, which opened in 1843; portland cement concrete was used in the world's first underwater tunnel.
1844 CE
Friedrich Engels publishes working class conditions
Friedrich Engels published 'The Condition of the Working Class in England' in 1844, describing the poor living conditions in industrial cities. This influential work exposed the harsh realities of industrial life and contributed to socialist thought.
Additional Factory Act passed
An additional Factory Act was passed in 1844, further restricting child labor and improving working conditions. These laws built upon the 1833 Factory Act to provide better protection for young workers in industrial settings.
1845 CE
R. White's Lemonade begins operations
R. White's Lemonade, a soft drinks company, began in 1845 by selling drinks in London from a wheelbarrow. This represents the growth of new consumer industries and street commerce during the Industrial Revolution.
1847 CE
Fry's produces first chocolate bar
Fry's of Bristol produced the first chocolate bar in 1847. This innovation in confectionery represented the transformation of luxury goods into mass-produced items affordable to broader segments of the population during industrialization.
1848 CE
Stock company law enacted in Sweden
A stock company law was enacted in Sweden in 1848, representing important institutional changes that supported industrialization. This legal framework facilitated business formation and investment in industrial enterprises.
1850 CE
Music halls develop in urban areas
Music halls developed in the 1850s as urbanization created new communities cut off from cultural roots, requiring new and accessible forms of entertainment. This represented the cultural adaptation to industrial urban life.
Sweden abolishes trade monopolies and joins gold standard
Sweden abolished most tariffs and barriers to free trade in the 1850s and joined the gold standard in 1873. These economic reforms supported Sweden's industrial development and integration into the global economy.
Waltham-Lowell system replaced by immigrant labor
By 1850, especially following the Great Famine of Ireland, the utopia-like Waltham-Lowell system was replaced by poor immigrant labor. This marked a significant change in American industrial labor practices and working conditions.
1851 CE
Great Exhibition held at Crystal Palace
The Great Exhibition was held at the Crystal Palace in 1851, showcasing industrial achievements and innovations. The Crystal Palace itself demonstrated new construction techniques using sheet glass and iron, symbolizing industrial progress.

The Crystal Palace housed the Great Exhibition of 1851
The Crystal Palace housed the Great Exhibition of 1851
1854 CE
John Snow traces cholera outbreak
In 1854, John Snow traced a cholera outbreak in Soho, London to fecal contamination of a public water well. His finding that cholera could be spread by contaminated water led to fundamental changes in public water and waste system design.
Watch industry industrialization begins
The industrialization of the watch industry started in 1854 in Waltham, Massachusetts, at the Waltham Watch Company. This involved developing machine tools, gauges and assembling methods adapted to the micro precision required for watches.
1855 CE
Metropolitan Board of Works begins London sewer system
The Metropolitan Board of Works, led by chief engineer Joseph Bazalgette, began construction of the modern sewage system in London in 1855. This massive public health project addressed sanitary conditions brought on by industrialization and urbanization.
1859 CE
London sewer system construction begins
The London sewer system began construction in 1859, including 82 miles of main sewers and 1,100 miles of street sewers. This revolutionary system diverted waste to the Thames Estuary and by the 1890s featured biological treatment of sewage.
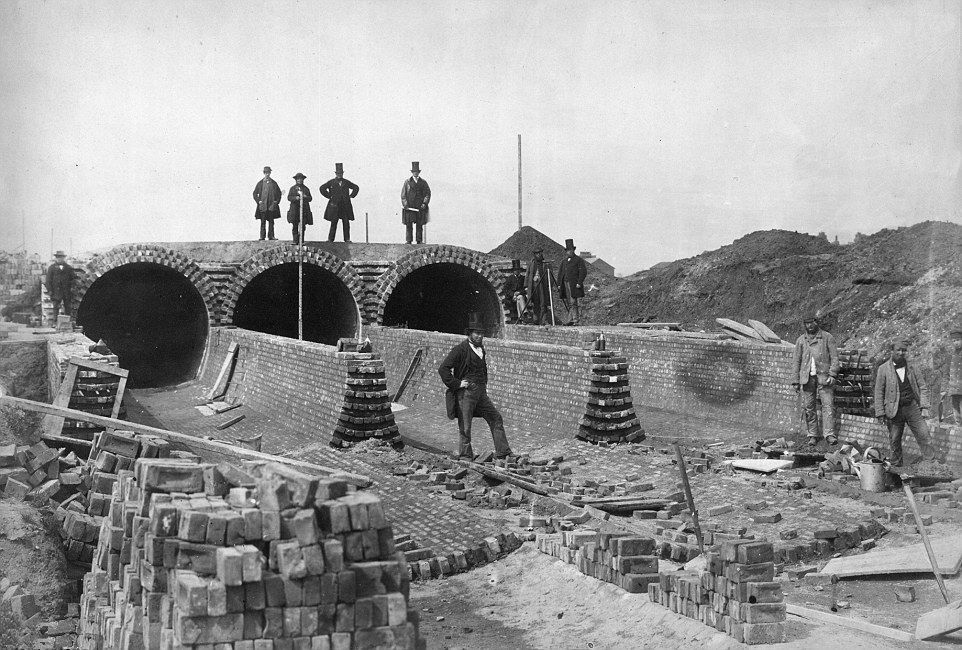

The London sewer system being built in 1860
The London sewer system being built in 1860 led by the chief engineer Joseph Bazalgette (top right)
1860 CE
Germany takes leadership in chemical industry
After 1860, the focus on chemical innovation shifted to dyestuffs, and Germany took leadership, building a strong chemical industry. Aspiring chemists flocked to German universities to learn the latest techniques, while British scientists lacked research universities.
Fish and chip shops first appear
In the 1860s, fish and chip shops first appeared to satisfy the needs of the growing industrial population. This represents the development of new food industries and urban dining culture during industrialization.
Henry Bessemer invents steel furnace
Henry Bessemer invented a new furnace in the 1860s that could convert molten pig iron into steel in large quantities. This innovation marked the beginning of the Second Industrial Revolution and mass steel production, though it only became widely available in the 1870s.
1861 CE
Pryce Pryce-Jones forms first mail order business
Welsh entrepreneur Pryce Pryce-Jones formed the first mail order business in 1861, selling Welsh flannel through catalogues. Customers could order by mail and goods were delivered via the railway system, revolutionizing retail.
1863 CE
Britain's Alkali Act regulates air pollution
Britain's Alkali Act of 1863 was passed to regulate air pollution from the Leblanc process used to produce soda ash. This was among the first large-scale modern environmental laws, with alkali inspectors appointed to curb pollution.
1867 CE
Reform Act extends franchise
The Reform Act of 1867 extended the franchise in Britain, allowing trades unions to begin supporting socialist parties after achieving effective political organization. This political reform enabled greater working-class representation.
Austria-Hungary formed
The Habsburg realms became Austria-Hungary in 1867. The empire had grown from 23 million people in 1800 to 36 million by 1870, with industrial development varying across regions but accelerating after this political reorganization.
1868 CE
Cadbury produces heart-shaped chocolate box
Cadbury of Birmingham produced a heart-shaped box of chocolates for Valentine's Day in 1868, becoming the first to commercialize the association between confectionery and romance. This represents the development of modern marketing and consumer culture.
1870 CE
Meiji period begins in Japan
The Industrial Revolution began in Japan around 1870 as Meiji period leaders decided to catch up with the West. The government built railways, improved roads, inaugurated land reform, and established a Western-based education system.
Parliament official emphasizes education importance
A senior government official told Parliament in 1870 that industrial prosperity depended on elementary education provision. This recognition of education's role in industrial competitiveness led to increased investment in public schooling.
Rapid growth resumes after 1870
Rapid economic growth resumed after 1870, driven by new innovations of the Second Industrial Revolution. These included steel-making processes, mass production, assembly lines, electrical grid systems, and large-scale manufacture of machine tools.
Steel becomes widely available
Steel became widely available in the 1870s after the Bessemer process was modified to produce more uniform quality. This marked the true beginning of the steel age and the Second Industrial Revolution's impact on construction and manufacturing.
1871 CE
Iwakura Mission tours Europe and US
In 1871, the Iwakura Mission, a group of Japanese politicians, toured Europe and the US to learn Western ways. This resulted in a deliberate state-led industrialization policy to enable Japan to quickly catch up with Western industrial powers.
German unification stimulates railway growth
German unification in 1871 stimulated consolidation, nationalization into state-owned companies, and further rapid railway growth. Unlike France, the goal was supporting industrialization with heavy lines crisscrossing the Ruhr and connecting major ports.
1873 CE
Sweden joins gold standard
Sweden joined the gold standard in 1873, completing economic reforms that included abolishing trade barriers in the 1850s. This monetary policy supported Sweden's integration into the global economy and industrial development.
1875 CE
Public Health Act requires smoke consumption
The Public Health Act of 1875 required all furnaces and fireplaces to consume their smoke and provided sanctions against factories emitting large amounts of black smoke. This environmental legislation addressed industrial pollution concerns.
1881 CE
Arnold Toynbee popularizes Industrial Revolution term
Arnold Toynbee's 1881 lectures gave a detailed account of the Industrial Revolution term, and he is credited with its popularization. His academic work helped establish the concept as a recognized historical period and phenomenon.
1882 CE
Bank of Japan founded
The Bank of Japan was founded in 1882, using taxes to fund model steel and textile factories. This state-led approach to industrialization helped Japan rapidly develop modern industry and catch up with Western industrial powers.
1885 CE
Further franchise extension
The franchise was extended again in 1885, allowing trades unions to support socialist parties that eventually merged to become the British Labour Party. This political development gave working people greater representation in government.
1890 CE
Electricity and electrification revolution begins
By the 1890s, a new revolution began with electricity and electrification in the electrical industries. This marked another phase of the Second Industrial Revolution, transforming power generation and industrial applications.
First giant industrial corporations emerge
By the 1890s, industrialization had created the first giant industrial corporations with global interests. Companies like U.S. Steel, General Electric, Standard Oil and Bayer AG joined railroad and ship companies on world stock markets.
1894 CE
Manchester Ship Canal opens
The Manchester Ship Canal opened in 1894, becoming the world's largest ship canal and opening Manchester as a port. However, it never achieved commercial success and signaled canals as a dying transport mode in the railway age.
1898 CE
Coal Smoke Abatement Society formed
The Coal Smoke Abatement Society was formed in Britain in 1898, founded by artist William Blake Richmond who was frustrated with pollution from coal smoke. This environmental organization worked to address industrial air pollution.
1905 CE
Growth renewal after 1905
Economic growth renewed after 1905 according to Maurice Lévy-Leboyer's analysis of French industrialization. This marked the end of the economic slowdown period (1860-1905) and the beginning of renewed industrial expansion.
1930 CE
Industrial development continues to 1930
From 1890 to 1930, new industries developed focusing on domestic markets including mechanical engineering, power utilities, papermaking and textile. This period saw the maturation of industrial economies and diversification of manufacturing.