Comparing Timelines
Exploring the overlapping histories of "Abolitionism" and "Space Race".
Abolitionism
1315 - 2022

Space Race
1921 - 1991
1315 CE
France Outlaws Slavery in Metropolitan Territory
Louis X, king of France, published a decree proclaiming that 'France signifies freedom' and that any slave setting foot on French soil should be freed. This was the first country to fully outlaw slavery, though it was later used in French colonies. The decree established the principle that French soil was incompatible with slavery.
1542 CE
Spain Enacts New Laws Abolishing Indigenous Slavery
Spain passed the New Laws in 1542, which abolished native slavery for the first time in European colonial history. This legislation was influenced by Bartolomé de las Casas' advocacy for indigenous rights and his book 'A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies'. The laws represented the first systematic attempt to protect indigenous peoples from enslavement.
1569 CE
English Court Rules Against Slavery Recognition
An English court considered the case of Cartwright, who had bought a slave from Russia, and ruled that English law could not recognize slavery as it was never established officially. This early legal precedent challenged the legitimacy of slavery under English common law, though it was later overshadowed by subsequent developments.
1590 CE
Japan Abolishes Chattel Slavery
Under the actions of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, chattel slavery was abolished across Japan. This made Japan one of the earliest countries to systematically eliminate slavery, though other forms of forced labor continued to be used, particularly during World War II. The abolition represented a significant shift in Japanese social policy.
1700 CE
Lord Chief Justice Holt Upholds Anti-Slavery Ruling
Lord Chief Justice John Holt ruled that a slave became free as soon as he arrived in England, upholding the earlier 1569 precedent. This decision reinforced the principle that English common law did not recognize slavery, setting important legal groundwork for future abolitionist arguments in British courts.
1755 CE
First Scottish Freedom Suit Filed
The case of Montgomery v. Sheddan took place in Scotland, representing one of the first freedom suits in the British Isles to challenge the legality of slavery. The slave had been baptized in Scotland and challenged his enslavement, setting important legal precedents for future cases, though the case ended before a court decision due to the plaintiff's death.
1769 CE
Second Scottish Freedom Suit
The case of Spens v. Dalrymple was heard in Scotland, continuing the legal challenges to slavery in Scottish courts. Like the previous case, the enslaved person had been baptized in Scotland and challenged the legality of their bondage. These cases established important legal procedures that would later lead to successful outcomes for plaintiffs in similar situations.
1772 CE
Somerset's Case Establishes Anti-Slavery Precedent
Lord Mansfield delivered his landmark judgment in Somerset's Case, declaring that slavery had no basis in English common law. The case involved James Somerset, a fugitive slave whose master attempted to ship him to Jamaica. Mansfield's decision was widely interpreted as prohibiting slavery in England, though it did not apply to British overseas territories.

1777 CE
Vermont Abolishes Adult Slavery
Vermont became the first state in what would become the United States to abolish adult slavery through its constitution. As an independent republic from 1777 to 1791, Vermont's action preceded its joining the Union and represented the first systematic abolition of slavery in North America by a political entity.
1778 CE
Knight v. Wedderburn Extends Anti-Slavery Law to Scotland
The Court of Session of Scotland ruled in Knight v. Wedderburn that chattel slavery was not recognized under Scottish law. Joseph Knight, an enslaved African brought from Jamaica, successfully argued for his freedom. The court declared that slaves could seek court protection to leave a master or avoid being forcibly removed from Scotland.
1780 CE
Pennsylvania Passes Gradual Emancipation Act
Pennsylvania became the first U.S. state to pass legislation for the gradual abolition of slavery. The act provided that no new slaves could be imported and that children born to enslaved mothers would eventually be freed, though existing slaves remained in bondage. This pioneering legislation served as a model for other northern states.
1787 CE
Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade Founded
The Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade was formed in London, marking the beginning of organized British abolitionist activism. This society would become instrumental in the parliamentary campaign against the slave trade, with members like William Wilberforce and Thomas Clarkson leading the movement.
1788 CE
Society of the Friends of the Blacks Established
Jacques Pierre Brissot founded the Society of the Friends of the Blacks (Société des Amis des Noirs) in Paris to work for the abolition of slavery. This organization played a crucial role in building anti-slavery sentiment in France and would influence the revolutionary government's decision to abolish slavery in 1794.

1791 CE
Haitian Revolution Begins
The slave revolt in Saint-Domingue began, marking the start of what would become the Haitian Revolution. Led by formerly enslaved people like Georges Biassou, Toussaint L'Ouverture, and Jean-Jacques Dessalines, this revolution would ultimately lead to Haiti becoming the first nation to achieve independence through a successful slave revolt.
1792 CE
Denmark Decrees End to Transatlantic Slave Trade
Denmark became the first country to issue a decree to abolish their transatlantic slave trade, effective from the start of 1803. While this was a significant step, Denmark would not abolish slavery in the Danish West Indies until 1848. The decree represented the first national commitment to ending participation in the Atlantic slave trade.
France Grants Citizenship to Free People of Color
Following the French Revolution, France granted free people of color full citizenship on April 4, 1792. This significant step toward racial equality preceded the complete abolition of slavery and represented a major advancement in civil rights for people of African descent in French territories.
1793 CE
Upper Canada Passes Act Against Slavery
Upper Canada passed the Act Against Slavery under Lieutenant Governor John Graves Simcoe, becoming the first legislation against slavery in the British Empire. The act prohibited the importation of new slaves and provided for the gradual emancipation of existing slaves, with children of enslaved mothers to be freed at age 25.
First Modern Emancipation Proclamation Issued
French Civil Commissioners Léger-Félicité Sonthonax and Étienne Polverel issued the first emancipation proclamation of the modern world (Decree of 16 Pluviôse An II) in Saint-Domingue. This proclamation was a crucial military strategy that brought most black troops into the French fold during the Haitian Revolution.
1794 CE
France Abolishes Slavery in All Territories
The French National Convention, under the leadership of Maximilien Robespierre, abolished slavery in law in France and its colonies on February 4, 1794. This was the first general abolition of slavery by a major European power, though Napoleon would later restore it in 1802. The law provided for compensation to slave owners.
1802 CE
Colonel Delgrès Leads Guadeloupe Rebellion
Colonel Delgrès launched a rebellion in Guadeloupe against Napoleon's representative, General Richepanse, in response to the re-establishment of slavery. The rebellion was ultimately repressed, and slavery was re-established in the colony. This resistance demonstrated the fierce opposition to the restoration of bondage.
Napoleon Re-establishes Slavery in French Colonies
Napoleon Bonaparte promulgated the law of May 20, 1802, re-establishing slavery in French colonies after becoming First Consul. This decision was influenced by pressure from planters, concerns about colonial revenues, and his wife's slaveholder family connections. Military governors and troops were sent to enforce the restoration of slavery.
1804 CE
Haiti Declares Independence and Abolishes Slavery
Haiti formally declared independence from France, becoming the first nation in the Western Hemisphere to permanently eliminate slavery in the modern era following the successful Haitian Revolution. This achievement made Haiti the first and only country to self-liberate from slavery through revolution, establishing a precedent for anti-colonial movements worldwide.
All Northern U.S. States Abolish Slavery
By 1804, all northern states in the United States had passed legislation abolishing slavery, though this did not immediately free all enslaved people. Some had to continue working as indentured servants for up to two more decades, and the process of gradual emancipation varied by state. This created a clear geographical division between free and slave states.
1807 CE
British Parliament Passes Slave Trade Act
The British Parliament passed the Slave Trade Act on March 25, 1807, making the slave trade illegal throughout the British Empire. While this did not immediately free existing slaves, it marked a crucial step toward complete abolition and established Britain as a leader in the international campaign against the slave trade.
1808 CE
United States Outlaws Slave Importation
The United States outlawed the importation of slaves, joining the international movement to end the Atlantic slave trade. However, this law did not affect the domestic slave trade or free existing slaves, and slavery continued to expand westward. The law represented a compromise between anti-slavery and pro-slavery factions.
1811 CE
Chile Declares Freedom of Wombs
Chile declared freedom of wombs, meaning that children born to enslaved mothers would be free. This represented an early step toward gradual emancipation in Latin America during the wars of independence. The policy was part of broader liberal reforms implemented by the new republican government.
1813 CE
United Provinces of River Plate Enacts Freedom of Wombs
The United Provinces of the River Plate (modern-day Argentina) followed Chile's example by declaring freedom of wombs in 1813. This policy ensured that children born to enslaved mothers would be free, representing a significant step toward gradual emancipation in the region during the independence period.
1821 CE
Colombia and Venezuela Declare Freedom of Wombs
Colombia and Venezuela implemented freedom of womb laws, continuing the pattern of gradual emancipation across newly independent Latin American republics. These laws were part of the broader liberal agenda of the independence movements, though complete abolition would take several more decades to achieve.
1823 CE
Chile Completely Abolishes Slavery
Chile became one of the first Latin American countries to completely abolish slavery, moving beyond the gradual emancipation policies of the previous decade. This decisive action reflected the influence of liberal ideology and the practical needs of building a new republican society based on principles of equality.
First Anti-Slavery Society Founded in Britain
The Society for the Mitigation and Gradual Abolition of Slavery Throughout the British Dominions was founded, marking the revival of the abolitionist movement to campaign against the institution of slavery itself, not just the slave trade. Many members had previously campaigned against the slave trade and now focused on complete emancipation.
1825 CE
France Recognizes Haiti and Imposes Indemnity
France finally recognized Haiti's independence but forced the nation to pay substantial reparations for losses during the revolution. This indemnity, which Haiti could ill afford, became a major cause of the country's enduring poverty and was not fully paid off until 1947. The recognition came with a heavy economic price.
1833 CE
Slavery Abolition Act Passed in Britain
The British Parliament passed the Slavery Abolition Act on August 28, 1833, which purchased slaves from their masters and paved the way for the abolition of slavery throughout the British Empire by 1838. This landmark legislation represented the culmination of decades of abolitionist campaigning and established Britain as a global leader in emancipation.

1837 CE
Elijah Parish Lovejoy Murdered by Pro-Slavery Mob
Abolitionist newspaper editor Elijah Parish Lovejoy was murdered by a pro-slavery mob in Alton, Illinois, on November 7, 1837. His death was covered in newspapers nationwide and caused a significant rise in membership in abolitionist societies. Lovejoy became a martyr for the anti-slavery cause and galvanized Northern opposition to slavery.
1839 CE
British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society Founded
Joseph Sturge founded the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society, which attempted to outlaw slavery worldwide and pressure the government to help enforce the suppression of the slave trade. This organization, which continues today as Anti-Slavery International, became the world's oldest international human rights organization.
1840 CE
World Anti-Slavery Convention Held in London
The British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society organized the World Anti-Slavery Convention at Exeter Hall in London from June 12-23, 1840. This was the first international attempt to address the abolition of slavery, bringing together delegates from around the world. Thomas Clarkson was the key speaker at this historic gathering.

1843 CE
Wallachia and Moldavia Begin Roma Emancipation
The principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia began the process of emancipating all 250,000 enslaved Roma people between 1843 and 1855. This progressive pro-European and anti-Ottoman movement worked systematically to abolish the legal slavery of the Roma population, representing a significant human rights achievement in Eastern Europe.
1848 CE
Denmark Abolishes Slavery in West Indies
Denmark finally abolished slavery in the Danish West Indies in 1848, completing the process that began with the 1792 decree to end the slave trade. This action eliminated one of the last remaining European slave systems in the Caribbean and demonstrated the continuing international pressure for complete emancipation.
France Permanently Abolishes Slavery
Under the Second Republic, France permanently abolished slavery in its remaining colonies on April 27, 1848, through a decree-law written by Victor Schœlcher. The state purchased the slaves from the colonists and then freed them, ensuring that this abolition would be permanent and comprehensive across all French territories.

1851 CE
Colombia Abolishes Slavery
Colombia completely abolished slavery in 1851, moving beyond the gradual emancipation policies implemented during the independence period. This decisive action reflected the growing influence of liberal ideology and international pressure for complete emancipation throughout Latin America.
1853 CE
Argentina Abolishes Slavery
Argentina abolished slavery with the signing of the Argentine Constitution of 1853, completing the gradual emancipation process that began during the independence period. This constitutional provision ensured that slavery would be permanently prohibited throughout the Argentine Republic.
1854 CE
Peru Abolishes Slavery
Peru abolished slavery in 1854, joining the growing number of Latin American republics that had eliminated the institution. This action was part of the broader liberal reforms sweeping across the region and reflected the influence of international abolitionist movements on Latin American politics.
Venezuela Abolishes Slavery
José Gregorio Monagas abolished slavery in Venezuela in 1854, completing the emancipation process that began with freedom of womb laws in 1821. This action eliminated one of the last remaining slave systems in northern South America and demonstrated the continuing influence of liberal ideology in the region.

1855 CE
Wallachia and Moldavia Complete Roma Emancipation
The principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia completed the emancipation of all 250,000 enslaved Roma people by 1855. This systematic process, which began in 1843, represented one of the most comprehensive ethnic emancipation programs in European history and eliminated a centuries-old system of Roma bondage.
1861 CE
Russia Emancipates the Serfs
Russia emancipated its serfs in 1861, ending centuries of feudal bondage for millions of peasants. This major social reform was implemented by Tsar Alexander II and represented one of the largest emancipation programs in history, though it failed to fully address rural and industrial unrest that would contribute to future revolutions.
1862 CE
District of Columbia Compensated Emancipation Act
Abraham Lincoln signed the District of Columbia Compensated Emancipation Act on April 16, 1862, abolishing slavery in Washington D.C. This act provided compensation to slave owners and represented the first federal legislation to free slaves in the United States, setting a precedent for broader emancipation measures.
Second Confiscation Act Frees Rebel-Owned Slaves
Congress passed the second Confiscation Act on July 17, 1862, stating that escaped or liberated slaves belonging to anyone who participated in or supported the rebellion 'shall be deemed captives of war, and shall be forever free of their servitude.' This act significantly expanded the scope of emancipation during the Civil War.
1863 CE
Lincoln Issues Emancipation Proclamation
Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863, changing the legal status of 3 million slaves in the Confederacy from 'slave' to 'free.' Though limited in scope, this executive order transformed the Civil War into a war for freedom and allowed freed slaves to join the Union army.
1864 CE
Maryland Abolishes Slavery
The state of Maryland abolished slavery on October 13, 1864, as part of the broader emancipation process during the American Civil War. Maryland was one of the border states that remained in the Union but maintained slavery until state-level abolition measures were implemented.
1865 CE
Missouri Abolishes Slavery
Missouri abolished slavery on January 11, 1865, eliminating bondage in another border state that had remained in the Union during the Civil War. This action preceded the ratification of the 13th Amendment and demonstrated the momentum toward complete emancipation throughout the United States.
West Virginia Fully Abolishes Slavery
West Virginia, which had been admitted to the Union in 1863 as a slave state with the condition of gradual emancipation, fully abolished slavery on February 3, 1865. This action completed the emancipation process in the state and eliminated slavery in another border region.
Juneteenth - Union Army Liberates Texas Slaves
On June 19, 1865, known as 'Juneteenth,' the Union Army gained control of Texas and liberated the last enslaved people in the Confederacy. This date became a symbol of emancipation and is now celebrated as a federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States.
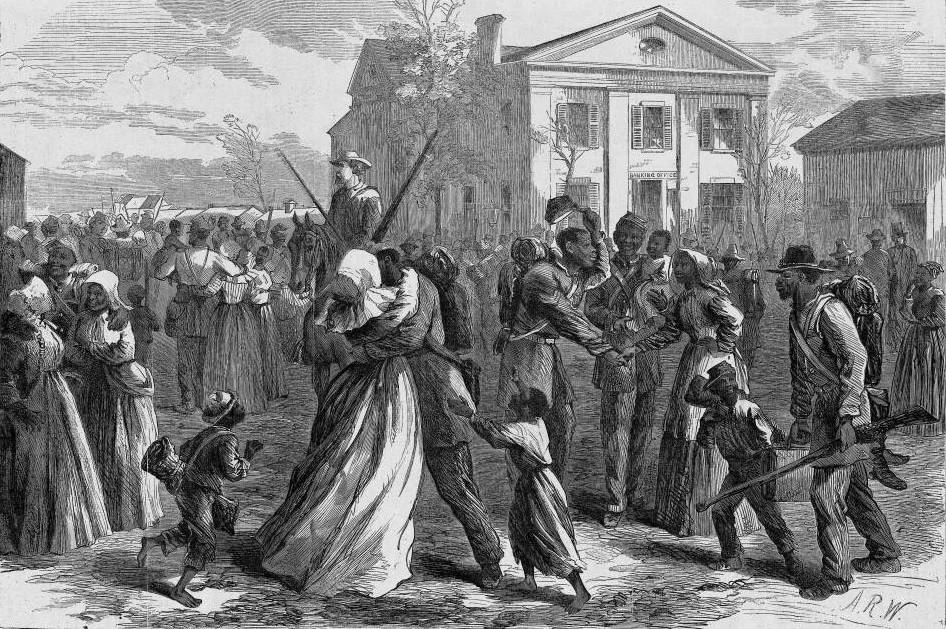

13th Amendment Ratified
The 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution took effect in December 1865, finally ending slavery for non-criminals throughout the United States. The amendment also abolished slavery among Indian tribes and represented the constitutional culmination of the American abolitionist movement, though it included an exception for punishment of crime.
1873 CE
Puerto Rico Abolishes Slavery
Puerto Rico abolished slavery in 1873, eliminating bondage in one of the last Spanish Caribbean colonies to maintain the institution. This action was part of Spain's gradual retreat from slavery in its remaining colonial territories and reflected growing international pressure for complete emancipation.
1886 CE
Cuba Abolishes Slavery
Cuba abolished slavery in 1886, eliminating bondage in one of the last major slave societies in the Americas. The abolition came after years of gradual emancipation policies and represented the end of Spanish colonial slavery in the Caribbean, leaving only Brazil as the final holdout in the Western Hemisphere.
1888 CE
Brazil Abolishes Slavery - Last in the Americas
Brazil abolished slavery in 1888 with the Lei Áurea (Golden Law), becoming the last country in the Americas to outlaw the institution. This action eliminated the largest slave system in the Western Hemisphere and marked the complete end of legal slavery in the Americas, concluding nearly four centuries of Atlantic slavery.

1890 CE
Brussels Conference Act Addresses Global Slavery
The Brussels Anti-Slavery Conference concluded with the Brussels Conference Act of 1890, representing the first major international governmental effort to address slavery on a semi-global level. The conference brought together representatives of colonial powers to coordinate anti-slavery efforts and establish international protocols.
1905 CE
France Abolishes Slavery in West Africa
France abolished slavery in most of French West Africa in 1905, though the abolition was not strictly enforced and some territories continued practicing slavery until later dates. This action was part of France's broader colonial policy but faced practical challenges in implementation across diverse African societies.
1921 CE
Soviet Gas Dynamics Laboratory Established
The Soviet military sanctioned the Gas Dynamics Laboratory, a small research laboratory to explore solid-fuel rockets, led by Nikolai Tikhomirov. This marked the beginning of organized Soviet rocket development efforts.
1924 CE
League of Nations Establishes Temporary Slavery Commission
The League of Nations founded the Temporary Slavery Commission (TSC) in 1924 to conduct a global investigation of slavery and slave trade worldwide. This commission represented the first systematic international effort to document and address slavery on a global scale, leading to important international treaties.
1926 CE
1926 Slavery Convention Adopted
The 1926 Slavery Convention was adopted based on the investigation of the Temporary Slavery Commission, representing a turning point in banning global slavery. This international treaty established legal frameworks for combating slavery worldwide and created binding obligations for signatory nations to eliminate the institution.
1928 CE
First Soviet Solid Fuel Rocket Test
The first test-firing of a solid fuel rocket was carried out by the Soviet Gas Dynamics Laboratory. This represented an early milestone in Soviet rocket technology development.
1932 CE
League Forms Committee of Experts on Slavery
The League of Nations formed the Committee of Experts on Slavery (CES) in 1932 to review the results and enforcement of the 1926 Slavery Convention. This committee conducted new international investigations and led to the establishment of the first permanent slavery committee, demonstrating continued international commitment to abolition.
1933 CE
First Soviet Liquid-Fueled Rocket Launch
Soviet rocket pioneers Sergey Korolev, Friedrich Zander, Mikhail Tikhonravov and Leonid Dushkin launched GIRD-X, the first Soviet liquid-fueled rocket. This achievement demonstrated Soviet progress in advanced rocket technology.
1934 CE
Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery Established
The Advisory Committee of Experts on Slavery (ACE) was established in 1934 as the first permanent international slavery committee. Between 1934 and 1939, the ACE conducted major international investigations on slavery and slave trade, inspecting all colonial empires and territories under their control.
1936 CE
Soviet Rocket Development Damaged by Great Purge
Joseph Stalin's Great Purge severely damaged Soviet rocket technology progress. Many scientists and engineers were imprisoned or executed, setting back the Soviet rocket program significantly.
1948 CE
UN Universal Declaration Bans Slavery
Article 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted in 1948 by the UN General Assembly, explicitly banned slavery worldwide. This declaration established slavery prohibition as a fundamental human right and created the moral and legal foundation for modern anti-slavery efforts.
1949 CE
First Mammal in Space
Albert II, a rhesus monkey, became the first mammal in space when launched by the US on a sub-orbital flight. The monkey died on landing due to a parachute malfunction, but the mission demonstrated the possibility of sending living creatures to space.
Soviet Union Becomes Second Nuclear Power
The Soviet Union became the second nuclear power after the United States with the successful RDS-1 nuclear weapon test. This achievement intensified the Cold War arms race and provided the backdrop for the space competition.
1950 CE
UN Ad Hoc Committee on Slavery Inaugurated
The Ad Hoc Committee on Slavery of the United Nations was inaugurated in February 1950, continuing the investigation of global slavery conducted by the League of Nations. This committee worked to develop new international instruments to combat slavery and ultimately led to the 1956 Supplementary Convention.
Soviet R-1 Rocket Enters Service
The R-1, a Soviet copy of the German A-4 (V-2) rocket, entered service in the Soviet Army. This marked the beginning of operational Soviet ballistic missile capability.
1951 CE
Public Interest in Space Travel Sparked
Soviet rocketry engineer Mikhail Tikhonravov published 'Flight to the Moon' in the newspaper Pionerskaya pravda, describing a two-person interplanetary spaceship. This article sparked public interest in space travel and predicted space flight within 10-15 years.
1955 CE
US Announces Intent to Launch Satellites
James C. Hagerty, President Eisenhower's press secretary, announced that the United States intended to launch 'small Earth circling satellites' as part of the International Geophysical Year. This announcement marked the official beginning of the Space Race.
Soviet Union Responds to US Satellite Announcement
At the Sixth Congress of the International Astronautical Federation in Copenhagen, Soviet scientist Leonid I. Sedov announced the Soviet Union's intention to launch a satellite 'in the near future.' This response escalated the space competition.
Soviet Space Commission Established
Sergei Korolev succeeded in convincing the Soviet Academy of Sciences to establish a commission dedicated to achieving the goal of launching a satellite into Earth orbit before the United States. This can be viewed as the de facto start date of the space race.
1956 CE
UN Supplementary Convention on Abolition of Slavery
The United Nations 1956 Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery was convened to outlaw and ban slavery worldwide, including child slavery. This comprehensive treaty expanded the definition of slavery and created stronger international mechanisms for enforcement and cooperation in anti-slavery efforts.
1957 CE
R-7 ICBM First Successful Flight
The Soviet R-7 Semyorka flew 6,000 km and became the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile. This achievement gave the USSR the capability to strike US territory with nuclear weapons and provided the launch vehicle for future space missions.

Sputnik 1 Launched
The Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, into Earth orbit. This achievement shocked the world and marked the beginning of the Space Age, giving the USSR an early lead in the Space Race.

Sputnik 2 Launches with Laika
The Soviet Union launched Sputnik 2 carrying Laika, a dog, making her the first animal to orbit Earth. The mission demonstrated that living creatures could survive in space, though Laika died from stress and overheating during the flight.

Project Vanguard Launch Failure
The US Project Vanguard launch failed spectacularly at Cape Canaveral, exploding seconds after launch. The failure became an international joke with nicknames like 'Flopnik' and 'Kaputnik,' highlighting American struggles to match Soviet space achievements.
1958 CE
Explorer 1 Launched
The United States successfully launched Explorer 1, its first satellite, on a Juno I rocket. The satellite discovered the Van Allen radiation belt, marking America's first major scientific achievement in space and its entry into the Space Race.

NASA Established
President Eisenhower signed the National Aeronautics and Space Act, creating NASA from the National Advisory Committee on Aeronautics. This established a civilian space agency to coordinate America's space efforts and compete with the Soviet Union.
1959 CE
Luna 1 Launched
The Soviet Union launched Luna 1, the first spacecraft to reach the vicinity of the Moon, though it missed its target. This mission marked the beginning of lunar exploration and demonstrated Soviet capability for deep space missions.
Luna 2 Impacts Moon
Luna 2 became the first human-made object to reach the Moon when it successfully impacted the lunar surface. This achievement gave the Soviet Union another space first and demonstrated their growing capability in space exploration.
Luna 3 Photographs Far Side of Moon
Luna 3 successfully flew by the Moon and transmitted the first pictures of its far side. This historic achievement provided humanity's first glimpse of the Moon's hidden hemisphere and demonstrated advanced Soviet space technology.

1961 CE
Yuri Gagarin First Human in Space
Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to orbit Earth aboard Vostok 1, completing a 108-minute flight. This achievement shocked the world and gave the Soviet Union a major victory in the Space Race, prompting the US to accelerate its space program.

Alan Shepard First American in Space
Alan Shepard became the first American in space with a suborbital flight on Mercury-Redstone 3 (Freedom 7). Though not achieving orbit like Gagarin, Shepard demonstrated manual spacecraft control and marked America's entry into human spaceflight.

Kennedy Announces Moon Landing Goal
President John F. Kennedy announced the goal of landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to Earth before the end of the decade. This bold commitment transformed the Space Race and focused American efforts on the lunar landing mission.
1962 CE
Saudi Arabia and Yemen Abolish Slavery
In November 1962, Faisal of Saudi Arabia prohibited the owning of slaves, followed by the abolition of slavery in Yemen in 1962. These actions eliminated some of the last legal slave systems in the world and marked the end of institutional chattel slavery in most of the Arabian Peninsula.
John Glenn First American to Orbit Earth
Astronaut John Glenn became the first American to orbit Earth, completing three orbits in Friendship 7. This achievement helped restore American confidence in the Space Race and demonstrated that the US could match Soviet orbital capabilities.
Mariner 2 First Successful Interplanetary Mission
NASA's Mariner 2 became the first spacecraft to successfully fly by another planet when it passed Venus. This achievement marked the beginning of interplanetary exploration and demonstrated American capability in deep space missions.
1963 CE
Dubai Abolishes Slavery
Dubai abolished slavery in 1963, continuing the process of eliminating the last legal slave systems in the Arabian Peninsula. This action was part of the broader modernization efforts in the Gulf region and international pressure to end all forms of legal bondage.
Valentina Tereshkova First Woman in Space
Soviet cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova became the first woman in space aboard Vostok 6. Her three-day mission demonstrated that women could perform effectively in space and gave the Soviet Union another space first.
1964 CE
Voskhod 1 First Multi-Person Crew
The Soviet Union launched Voskhod 1 with a three-person crew, achieving the first spaceflight with multiple crew members. This mission beat the American Gemini program to this milestone and demonstrated Soviet spacecraft capabilities.
1965 CE
Alexei Leonov First Spacewalk
Soviet cosmonaut Alexei Leonov performed the first extravehicular activity (spacewalk) during the Voskhod 2 mission. This 12-minute spacewalk demonstrated human capability to work outside spacecraft, though Leonov nearly died when his spacesuit expanded.
Gemini 6 and 7 First Space Rendezvous
Gemini 6A and Gemini 7 achieved the first rendezvous between two crewed spacecraft, coming within one foot of each other. This achievement demonstrated critical technology needed for lunar missions and marked a turning point in American space capabilities.

1966 CE
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
The UN General Assembly adopted the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights in December 1966, with Article 4 banning slavery. The treaty came into force in March 1976 after ratification by 35 nations and created binding legal obligations for states to prohibit slavery and ensure civil rights.
Luna 9 First Soft Moon Landing
Luna 9 achieved the first soft landing on the Moon and successfully transmitted photography from the lunar surface. This achievement demonstrated that spacecraft could safely land on the Moon and provided the first close-up images of the lunar surface.

Venera 3 First Impact on Another Planet
Venera 3 became the first human-made object to impact another planet when it crashed on Venus. Though contact was lost before impact, this mission marked the beginning of planetary exploration and demonstrated Soviet deep space capabilities.
1967 CE
Apollo 1 Fire Kills Three Astronauts
A fire during a ground test of Apollo 1 killed astronauts Gus Grissom, Ed White, and Roger Chaffee. This tragedy led to major safety improvements in the Apollo program and delayed the first crewed Apollo mission by nearly two years.

Outer Space Treaty Signed
The United States, Soviet Union, and United Kingdom signed the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space. This treaty established space as the common heritage of mankind and prohibited weapons of mass destruction in space.
Vladimir Komarov Dies in Soyuz 1
Soviet cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov became the first in-flight spaceflight fatality when Soyuz 1's parachute system failed during reentry. This tragedy highlighted the dangers of space exploration and led to improvements in Soviet spacecraft design.

1968 CE
Apollo 8 First Humans to Leave Earth Orbit
Apollo 8 carried Frank Borman, James Lovell, and William Anders on the first crewed mission to leave Earth orbit and travel to the Moon. Their Christmas Eve broadcast from lunar orbit was one of the most watched TV programs in history.

1969 CE
Apollo 11 Moon Landing
Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to land on the Moon while Michael Collins orbited above. Armstrong's first steps on the lunar surface were watched by an estimated 723 million people worldwide, marking America's victory in the Space Race.

1970 CE
Oman Abolishes Slavery
Oman abolished slavery in 1970, becoming one of the last countries in the world to legally end the institution. This action eliminated one of the final remaining legal slave systems and marked the near-complete global abolition of institutional chattel slavery, with only a few countries remaining.
Venera 7 First Data from Another Planet's Surface
Soviet Venera 7 became the first spacecraft to successfully transmit data from the surface of another planet. The probe measured Venus's surface temperature at 475°C and atmospheric pressure at 92 bars, providing crucial data about Venus's hostile environment.
Luna 16 First Robotic Sample Return
Luna 16 became the first uncrewed spacecraft to return samples from the Moon to Earth. This achievement demonstrated that robotic missions could accomplish complex tasks and provided an alternative to crewed lunar exploration.
1971 CE
Mars 2 First Object to Impact Mars
Soviet Mars 2 became the first human-made object to impact Mars, though the lander crashed and was destroyed. This mission marked the beginning of Mars exploration and demonstrated the challenges of landing on the Red Planet.
Salyut 1 First Space Station
The Soviet Union launched Salyut 1, the world's first space station. Though the first crew died during reentry due to cabin depressurization, this achievement marked the beginning of long-duration spaceflight and orbital laboratories.
1973 CE
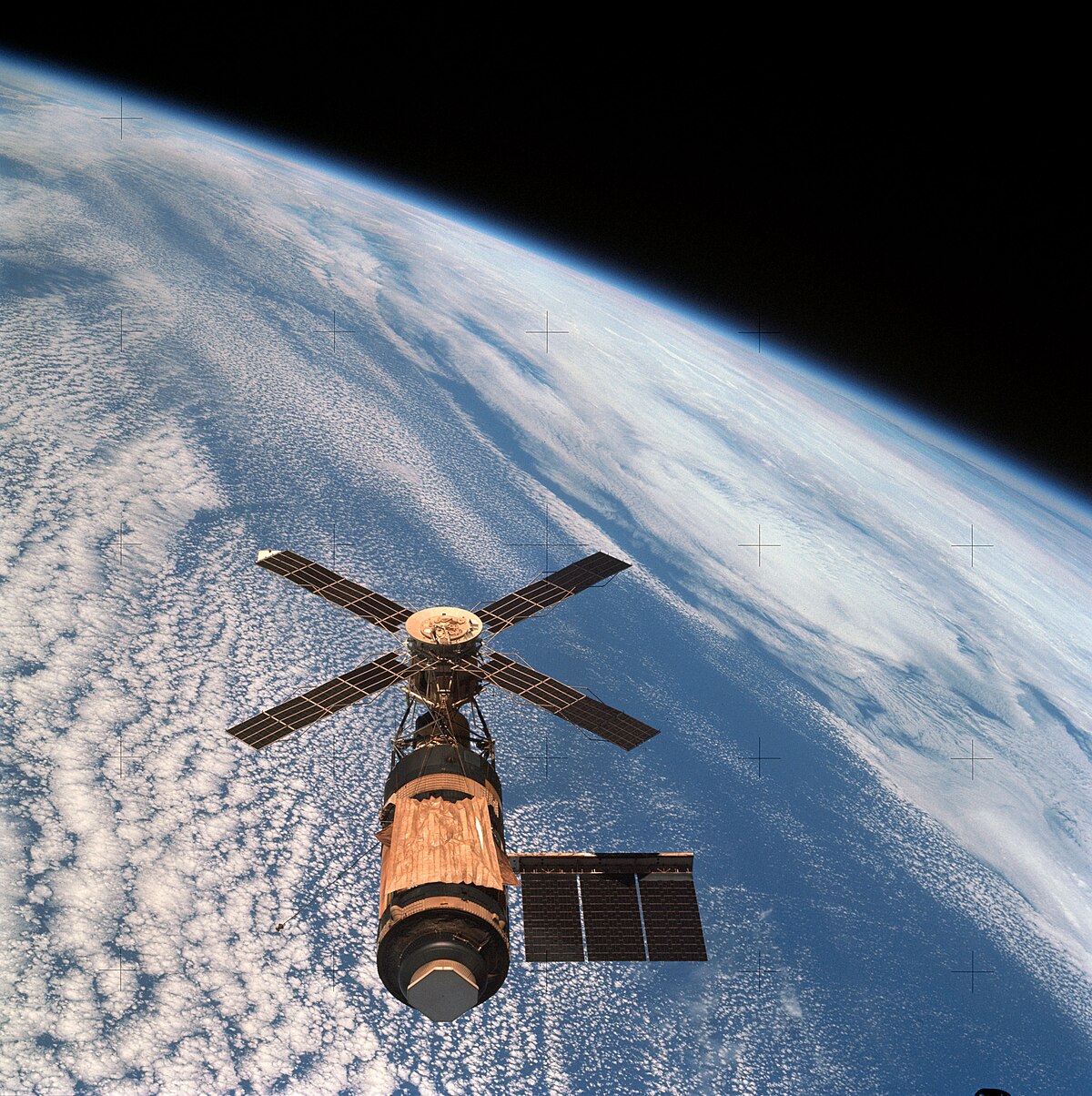
Skylab Launched
The United States launched Skylab, its first and only space station, using a Saturn V rocket. Despite initial damage during launch, Skylab hosted three crews and conducted valuable scientific research, demonstrating American capability in long-duration spaceflight.

1975 CE
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project
American and Soviet spacecraft docked in orbit for the first time, with crews shaking hands in space. This joint mission marked the symbolic end of the Space Race and the beginning of international cooperation in space exploration.

1976 CE
Viking 1 and 2 Land on Mars
NASA successfully landed two Viking spacecraft on Mars, taking the first photographs from the Martian surface and conducting extensive scientific analysis. These missions provided detailed information about Mars and demonstrated American leadership in planetary exploration.

1981 CE
Mauritania Officially Abolishes Slavery
Mauritania became the latest country to officially abolish slavery with a presidential decree in 1981, making it the last country in the world to legally prohibit the institution. However, slavery continues to persist illegally in Mauritania, with estimates suggesting that up to 20% of the population remains enslaved.
First Space Shuttle Flight
NASA's Space Shuttle Columbia completed its first orbital test flight, marking the beginning of the reusable spacecraft era. The Space Shuttle program represented a new approach to space access, though it proved more expensive and dangerous than initially planned.
1983 CE
Sally Ride First American Woman in Space
Sally Ride became the first American woman in space aboard Space Shuttle Challenger on STS-7. Her flight marked a significant milestone in gender equality in space exploration and inspired a generation of women to pursue careers in science and technology.
1986 CE
Mir Space Station Assembly Begins
The Soviet Union began assembling the Mir space station, which would become the largest spacecraft and maintain the longest continuous human presence in space. Mir represented the pinnacle of Soviet space station technology and international cooperation.

1988 CE
Buran Shuttle First Flight
The Soviet Union's Buran space shuttle completed its first and only orbital flight, flying unmanned and landing automatically. This achievement demonstrated Soviet capability to match American shuttle technology, though the program was canceled due to the USSR's collapse.

1991 CE
Soviet Union Collapses
The collapse of the Soviet Union effectively ended the Space Race as a competition between superpowers. The Russian Federation inherited most Soviet space assets, leading to increased cooperation with the United States in space exploration.
2000 CE
United States Passes Trafficking Victims Protection Act
The United States passed the Victims of Trafficking and Violence Protection Act (TVPA) in 2000 'to combat trafficking in persons, especially into the sex trade, slavery, and involuntary servitude.' The TVPA created new law enforcement tools and made human trafficking a federal crime with severe penalties.
2001 CE
France Recognizes Slavery as Crime Against Humanity
The Taubira law, passed on May 10, 2001, officially acknowledged slavery and the Atlantic slave trade as a crime against humanity in France. May 10 was chosen as the day dedicated to recognition of the crime of slavery, establishing an annual commemoration and formal acknowledgment of historical injustices.
2004 CE
UN Declares International Year Against Slavery
The United Nations General Assembly declared 2004 the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle against Slavery and its Abolition, marking the bicentenary of Haiti's independence. This proclamation led to numerous exhibitions, events, and research programs worldwide to commemorate abolitionist movements.
2014 CE
Religious Leaders Unite Against Modern Slavery
For the first time in history, major Anglican, Catholic, and Orthodox Christian leaders, as well as Jewish, Muslim, Hindu, and Buddhist leaders, met in 2014 to sign a shared commitment against modern-day slavery. Their declaration called for the elimination of slavery and human trafficking by 2020.
2018 CE
Colorado Removes Prison Labor Exception
In 2018, Colorado became the first state to remove language in its state constitution allowing slavery 'as punishment for crime' through a legislatively referred ballot referendum. This action began a movement to eliminate the 13th Amendment's exception for prison labor from state constitutions across the United States.
